February 9, 2016
Measuring Pancreatic Elastase to Diagnose Pancreatic Disease
Many digestive system disorders and diseases can present similar types of symptoms including bloating, diarrhea, constipation, and weight gain/loss. In an effort to rule in or rule out the presence of one disease or the absence of another, clinicians will often turn to clinically approved stool-based tests measuring different biomarkers. Measuring pancreatic elastase to diagnose pancreatic disease has become a more common practice by clinicians. Stool pancreatic elastase levels can help determine exocrine pancreatic function. The Pancreatic Elastase ELISA is a tool to confidently measure levels of pancreatic elastase in human stool samples.
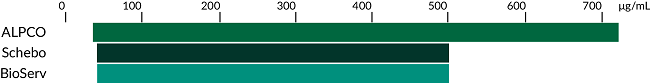 It is imperative to trust your results when testing levels of pancreatic elastase in stool. Our Pancreatic Elastase ELISA offers superior specificity compared to other assays on the market measuring stool pancreatic elastase. With the broadest range and the greatest sensitivity, fewer samples are rerun. The sandwich monoclonal antibody system provides increased specificity, allowing for greater confidence when measuring pancreatic elastase to diagnose pancreatic disease. The assay is compatible with our unique Easy Stool Extraction Device which saves researchers time and money in their stool extraction procedures.
It is imperative to trust your results when testing levels of pancreatic elastase in stool. Our Pancreatic Elastase ELISA offers superior specificity compared to other assays on the market measuring stool pancreatic elastase. With the broadest range and the greatest sensitivity, fewer samples are rerun. The sandwich monoclonal antibody system provides increased specificity, allowing for greater confidence when measuring pancreatic elastase to diagnose pancreatic disease. The assay is compatible with our unique Easy Stool Extraction Device which saves researchers time and money in their stool extraction procedures.
 Download Brochure
Download Brochure
Comprehensive Stool Analysis with the Easy Stool Extraction Device
The Easy Stool Extraction Device is an FDA Class I Exempt tool that can be used across four comprehensive gastroenterology ELISA testing panels comprised of 13 different analytes.
The device allows lab technicians to replace manual weighing with one simple step. A grooved plastic wand is dipped into a stool sample in multiple areas and placed inside a vial pre-filled with a universal extraction buffer. This standardized device accurately measures 15 mg of stool and extracts the sample in 1.5 mL of extraction buffer, yielding a final dilution of 1:100. The resulting extract can be placed directly on automated platforms and run across up to 13 different assays.
Measuring Pancreatic Elastase to Diagnose Pancreatic Disease
Pancreatic elastase is mainly bound to bile salts during intestinal passage and is not degraded1. As a result, pancreatic elastase levels in human stool are 5-6 fold more concentrated than in pancreatic juice1. The stool concentration reflects the secretory capacity of the pancreas. Stool pancreatic elastase is a marker used to define exocrine pancreatic function, with low levels indicating the presence of pancreatic insufficiency which can be the result of a number of different ailments such as chronic pancreatitis, pancreatic cancer, cystic fibrosis, diabetes and Crohn’s disease1. These factors have contributed towards the growth of measuring pancreatic elastase to diagnose pancreatic disease.Be Confident in Your Pancreatic Elastase ELISA Results
 It is imperative to trust your results when testing levels of pancreatic elastase in stool. Our Pancreatic Elastase ELISA offers superior specificity compared to other assays on the market measuring stool pancreatic elastase. With the broadest range and the greatest sensitivity, fewer samples are rerun. The sandwich monoclonal antibody system provides increased specificity, allowing for greater confidence when measuring pancreatic elastase to diagnose pancreatic disease. The assay is compatible with our unique Easy Stool Extraction Device which saves researchers time and money in their stool extraction procedures.
It is imperative to trust your results when testing levels of pancreatic elastase in stool. Our Pancreatic Elastase ELISA offers superior specificity compared to other assays on the market measuring stool pancreatic elastase. With the broadest range and the greatest sensitivity, fewer samples are rerun. The sandwich monoclonal antibody system provides increased specificity, allowing for greater confidence when measuring pancreatic elastase to diagnose pancreatic disease. The assay is compatible with our unique Easy Stool Extraction Device which saves researchers time and money in their stool extraction procedures.
 Download Brochure
Download Brochure
Comprehensive Stool Analysis with the Easy Stool Extraction Device 
The Easy Stool Extraction Device is an FDA Class I Exempt tool that can be used across four comprehensive gastroenterology ELISA testing panels comprised of 13 different analytes.
The device allows lab technicians to replace manual weighing with one simple step. A grooved plastic wand is dipped into a stool sample in multiple areas and placed inside a vial pre-filled with a universal extraction buffer. This standardized device accurately measures 15 mg of stool and extracts the sample in 1.5 mL of extraction buffer, yielding a final dilution of 1:100. The resulting extract can be placed directly on automated platforms and run across up to 13 different assays.
References
- Medscape. (2014). Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency. Medscape.com. Retrieved from http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2121028-overview#a8